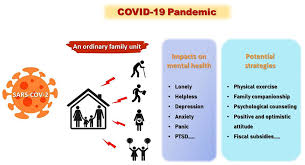
Mental Health Challenges During COVID-19 and Progress by 2025
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly impacted global mental health, leading to a significant rise in mental health disorders. In March 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported a 25% increase in the prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide during the first year of the pandemic. This surge was attributed to factors such as social isolation, fear of infection, and financial stress.
As of January 2025, while the acute phase of the pandemic has subsided, mental health challenges persist. The World Economic Forum’s Global Risks Report 2025 highlights a decline in health and well-being as a significant interconnected risk, emphasizing the ongoing mental health crisis. Additionally, the WHO’s 2025 Health Emergency Appeal underscores the widening gap in humanitarian funding, which affects the availability of mental health services.
Despite these challenges, there have been advancements. The rapid adoption of telemental health services during the pandemic has improved access to care for individuals with conditions like schizophrenia. Furthermore, global research initiatives have identified numerous genetic risk factors for depression, paving the way for more personalized treatments.
In conclusion, while some progress has been made in addressing mental health issues since the onset of the pandemic, significant challenges remain. Ongoing efforts are essential to enhance mental health services and support worldwide.
Sources
- WHO – COVID-19 pandemic triggers 25% increase in prevalence of anxiety and depression worldwide
- World Economic Forum – Mental Health: The Unexplored Side of the 2025 Global Risks Report
- WHO – WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the launch of WHO’s 2025 Health Emergency Appeal
- Medical Xpress – Pandemic led to rapid adoption of telemental health for those with schizophrenia
- The Guardian – Scientists find hundreds more genetic risk factors for depression